
However, continuous combustion engines, such as jet engines, most rockets and many gas turbines are also internal combustion engines.įor a typical four-stroke engine, key parts of the engine include the combustion chamber, one or more camshafts, cams and intake and exhaust valves. The term Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) is almost always used to refer specifically to reciprocating engines and similar designs in which combustion is intermittent. The most significant distinction between modem internal combustion engines and the early designs is the use of compression and in particular of in-cylinder compression. The first internal combustion engines did not have compression, but ran on air/fuel mixture sucked or blown in. This exothermic reaction of a fuel with an oxidizer creates gases of high temperature and pressure, which are permitted to expand. Intake- process of filling the cylinder with the proper air-fuel mixture through the intake valve.Ĭompression- the process of compressing the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder to make it more combustibleĬombustion-the process of igniting the compressed air-fuel mixture to create motion and the over all power of the engine.Įxhaust- the process of releasing the exhaust out of the cylinder through the exhaust valve.The internal combustion engine in which the combustion (or radip oxidation) of gas and air occurs in a confined space called a combustion chamber. Crankshaft- converts the up and down motion of the piston into a turning, or rotating motion Rod Bearing- used to reduce friction to the rod and crankshaft Connecting Rod- links the piston to the crankshaft. Piston- the part of the engine that moves up and down in the cylinder converting the gasoline into motion Exhaust Port- the passageway in a cylinder head, for the exhaust to pass through Spark Plug- a device, inserted into the combustion chamber for firing an electrical spark to ignite air-fuel mixture

Exhaust Valve- open at the proper time to release the exhaust
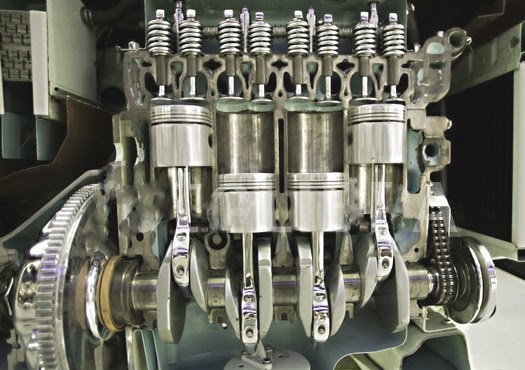
Camshaft- a round shaft with lobes, that rotates to open and close the fuel and exhaust valves. Oil Sump- the collected oil primarily for lubricating the crankshaft and rod bearing Oil Pan- where the oil is collected and recirculated. The basis for most of the parts of the engine. Coolant- circulating water and antifreeze to keep the temperature regulated.į.
Head- a platform containing most of the parts of the combustion chamber.Į.
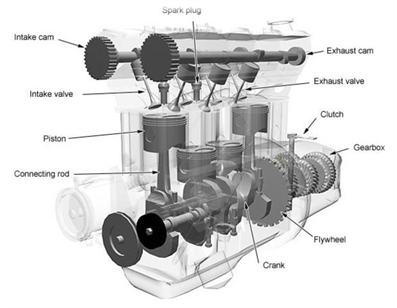
Intake Port- the passageway in a cylinder head for the fuel and air to pass through.ĭ. Valve Cover- Protects the valves and the valve springs. Intake Valve- opens at the proper time to let in air and fuel.ī. Intake ValveValve CoverIntake PortHeadCoolantEngine BlockOil PanOil SumpCrankshaftCamshaftExhaust ValveSpark PlugExhaust PortPistonConnecting RodRod BearingsĪ. Two-stroke enginesDiesel enginesRotary enginesTurbine enginesSteam engines Heat engine is a modified form of engine used for transforming chemical energy of fuel into thermal energy and subsequently for producing work.Ī four-stroke engine:Is an internal combustion engineConverts gasoline into motionIs the most common car engine typeIs relatively efficientIs relatively inexpensive Engine is a device which transforms one form of energy into the other form.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
